Prompt Engineering: An Integrated Dream
Image created by me with Microsoft Image Creator
Since OpenAI unleashed ChatGPT to the public, a flurry of discussions has emerged online about a new dream job: Prompt Engineering. It’s touted as “AI’s Hottest Job,” promising six-figure salaries without the need for programming experience. Enthusiasts describe it as a job of the future, where anyone can earn up to $335K by smooth-talking a cool know-it-all robot into giving right answers. No surprise, Instagram money making sages, YouTube career preachers, and self-proclaimed oracles of TikTok have been very vocal about it. While this sounds like a dream job, is it truly achievable? Let’s delve into the reality of job market behind the hype to find out.
Analyzing job advertisement data provides valuable insights into labor demand trends, responsibilities, qualifications, and salary expectations. Thus, I decided to take a look at the ad data of the so-called “AI’s Hottest Job” with no speculations or presumptions. I collected 73 recently posted unique job ads data from popular on-line job posting platforms. Read about my data collection methodology and access the data set here. While 73 may not be an ideal sample size, it’s a comprehensive starting point for our analysis. The initial revelation is sobering: there’s a scarcity of employers seeking “prompt engineers.”
Now, let’s take a look at the data. The most frequently mentioned job title is “prompt engineer.” However, other titles such as “IT Innovation Analyst,” “Freelance ML/AI Engineer,” “Data Scientist,” and “AI Engineer” also emerge. I created word clouds for qualifications and responsibilities mentioned in the job descriptions. I don’t think word clouds are meant to reveal extraordinary insights, but they can represent a compact version of the important highlights in the text. As you see, in the job ads employers are talking about experience in computer science, model development, python, prompt design, machine learning, large language models, natural language processing, and artificial intelligence more than other stuff.

1.This is a significantly larger sample size if you compare it with many of those anecdotal early articles who constructed their whole argument about a six-figure salary with no coding from only one job ad.
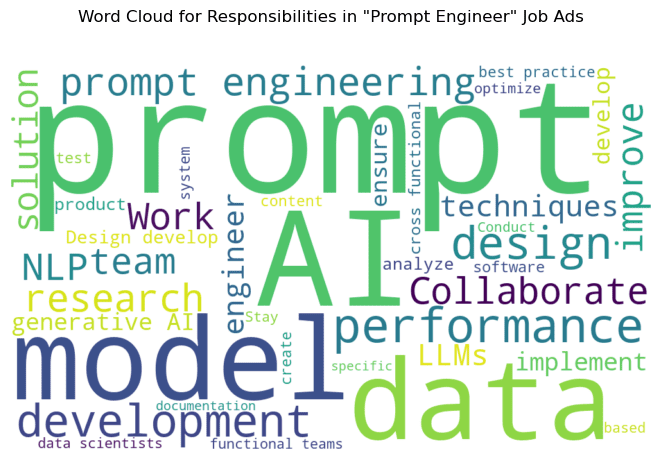
Next, I used ChatGPT and Claude to summarize the collected ads text corpus to identify top prompt engineering qualifications and qualifications. I did multiple rounds of prompting with different approaches followed by manually checking the data to make sure I got stable and valid output.
Essential qualifications demanded for Prompt Engineer job:
- Proficiency in Python programming (2-5 years of experience) including experience with AI/machine learning frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, Keras.
- Working knowledge of NLP and LLMs (2-5 years of experience) like BERT, GPT-3/4, T5, etc. Knowledge of how these models work and how to fine-tune them.
- Strong analytical and problem-solving skills. The ability to think critically, design effective prompts, analyze model performance, and troubleshoot issues is vital.
- Expertise in prompt engineering principles and techniques like chain of thought, in-context learning, tree of thought, etc. This allows guiding the models to desired outcomes.
- Excellent communication skills, both verbal and written. This is needed for collaborating across teams, explaining technical concepts, and documenting work.
And the essential responsibilities of the prompt engineering jobs are:
- Prompt Design and Optimization: Designing, developing, testing, and refining AI-generated text prompts to maximize effectiveness for various applications. This includes utilizing techniques like transfer learning and leveraging linguistic expertise to craft high-quality and diverse prompts.
- Integration and Deployment: Ensuring seamless integration of optimized prompts into the overall product or system. Collaborating with engineers to implement prompts and models into production environments.
- Performance Evaluation and Improvement: Rigorously evaluating prompt performance using metrics and user feedback. Conducting continuous testing and analysis to identify areas for optimization and prompt iteration.
- Collaboration and Requirements Gathering: Working closely with cross-functional teams like data scientists, content creators, and product managers to understand requirements and ensure prompts align with business goals and user needs.
- Knowledge Sharing: Documenting prompt engineering processes and outcomes. Educating teams on prompt best practices. Keeping updated on the latest AI advancements to bring innovative
It is fair to say that “no programming experience” premise of the so called “AI’s Hottest Job” is far from the reality, since the top demanded skills in the prompt engineering market are programming proficiency and NLP and LLMs experience. And they are not talking about micky mouse programming skills, they are looking for experts who are familiar with ML and AI frameworks. The employers are not just requiring “familiarity” with LLMs and coding, but, on average, they seek experts with 2-5 years of experience working with structured and unstructured data, coding, NLP, ML, and AI.
Reading the top responsibilities make it more clear why this job title demands such a high level of programming and LLMs skills. Prompt engineering, as a professional job, is not sitting behind a computer and playing with Generative AI models to give you the right answer. It is about building business information systems that optimize inputs, integrate them seamlessly with other information systems and products, and deliver values to users and customers. In other words, businesses are not looking for someone who can chat with ChatGPT, they want to hire experts who can optimize GPT-like models and integrate them with their own products.
Job ads data analysis of degree requirements indicates a preference for technical educational backgrounds in computer science, math, analytics, engineering, physics, or linguistics. A bachelor’s degree in computer science or a related field is commonly required, with more advanced degrees preferred or required for senior roles. The salaries are very different depending on the responsibilities and seniority. It can be as low as 30k and as high as half a million dollars per year. On average, the job ads with salary information pay between 90k and 195k a year.
Despite initial enthusiasm, doubts regarding the viability of prompt engineering as a dream job have surfaced. As Ethan Mollick, the Wharton School professor, wrote in a twitter post last year “prompt engineer is not a job of future” because “AI gets easier” and smarter in interpreting basic prompts. A month ago Coursera published a well-thought career guide for prompt engineering (also see this). It seems the initial Gen AI fad is slowly fading, and we are in a better position to understand AI’s current status and future trends. Don’t get me wrong. The quality of Gen AI outputs strongly depends on the inputs. Learning how to use and interact with these complex models is becoming an important skill for almost everyone. There are increasing number of scientific studies that suggest a systematic approach to prompting can significantly improve the outcome of these models (see 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7). However, “prompt engineering” is not (and it never was) a dream job that some people wanted it to be. Without significant experience in programming, natural language processing, machine learning, product development, and software integration no one is going to pay you a six-figure salary for just smooth-talking ChatGPT into a right answer.
The present and future of prompt engineering, and Gen AI applications, seem to be influenced by two important trends: first, as Ethan Mollick mentioned, Gen AI models are getting more adept at generating good outputs from unsophisticated simple prompt, perhaps similar to how Internet search engines have become better at returning more relevant results from simple search queries. Second, Gen AI models are being increasingly integrated into the business’s products, services, and platforms. This adaptation is crucial for the success of the AI economy. Therefore, knowing how to optimize, fine-tune, customize, and integrate Gen AI models with the current information systems and products is and will remain a valuable skill set. That’s why in the current prompt job ads, there is a huge demand for programmers, system designers, and those who can collaborate with other product development team members.
Mahdi Ahmadi is a clinical assistant professor at the Information Technology & Decision Sciences department at the University of North Texas where I teach data mining, business intelligence, and data analytics. My primary research area is the application of machine learning and data mining techniques in businesses. I also provide consultation to businesses, higher education institutions, and non-for-profit organizations on their data analytics problems.