Blockchain Technology in Healthcare Data Management
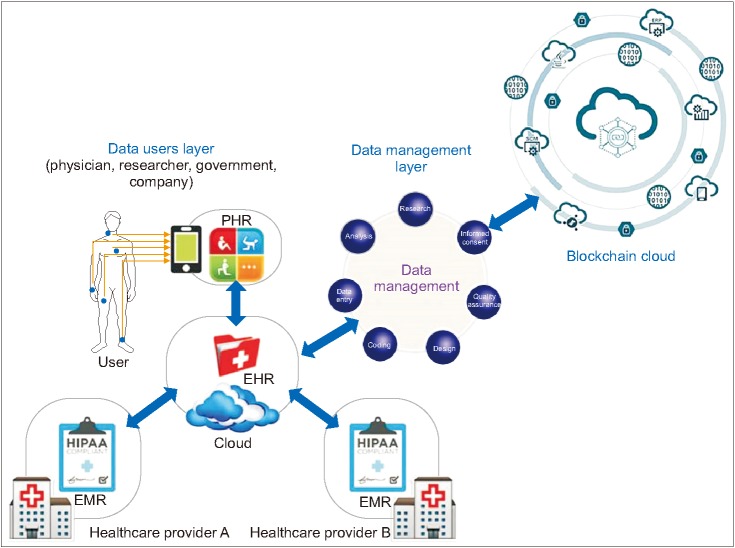
The healthcare industry is facing unprecedented challenges in the digital age. With the growing volume of patient data, the need for secure, efficient, and interoperable systems has become more critical than ever. Enter blockchain technology, a revolutionary innovation that has the potential to transform healthcare data management. In this article, we will explore how blockchain technology is revolutionizing the healthcare sector by improving data security, privacy, and interoperability while also addressing some of the industry’s most pressing issues.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Before diving into its applications in healthcare, it’s essential to understand what blockchain technology entails. At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized and immutable digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. These transactions are grouped into “blocks” and linked together to form a continuous chain. The distributed nature of this ledger ensures data security, transparency, and trust among participants.
Applications of Blockchain in Healthcare Data Management
- Secure Patient Records: Blockchain technology can securely store and manage electronic health records (EHRs) by encrypting them and granting access only to authorized individuals. Patients have more control over their data, ensuring their privacy and security.
- Interoperability: Healthcare data often resides in fragmented systems that do not communicate effectively. Blockchain can enable seamless data exchange among different healthcare providers, improving coordination and patient care.
- Data Integrity: Once healthcare data is recorded on a blockchain, it becomes tamper-proof. This ensures the accuracy and integrity of patient records, reducing the risk of medical errors and fraud.
- Consent Management: Patients can use blockchain to manage their consent for data sharing. They can grant and revoke access to their health information, giving them more control over who sees their data.
- Drug Traceability: Blockchain can track the provenance of pharmaceuticals and medical devices, reducing the risk of counterfeit drugs entering the supply chain.
- Clinical Trials: Smart contracts on the blockchain can automate various aspects of clinical trials, including participant recruitment, data collection, and payments, making trials more efficient and transparent.
Benefits of Blockchain in Healthcare Data Management
- Enhanced Data Security: Blockchain’s encryption and decentralized nature make it extremely secure. Patient data is protected against unauthorized access and tampering, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Patient Empowerment: Patients gain more control over their health data, allowing them to share it securely with healthcare providers and researchers while maintaining their privacy.
- Interoperability: Improved data sharing and interoperability lead to better coordination among healthcare providers, resulting in more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
- Reduced Administrative Costs: Blockchain streamlines administrative tasks and reduces paperwork, leading to cost savings for healthcare organizations.
- Data Transparency: All parties involved in a patient’s care can access the same data, promoting transparency and reducing errors caused by incomplete or outdated information.
Real-World Examples
Several initiatives and organizations are already harnessing blockchain technology for healthcare data management:
- MedRec: This MIT project uses blockchain to create a decentralized, patient-centered EHR system. Patients have control over their data, and healthcare providers can access it with patient consent.
- Medicalchain: Medicalchain uses blockchain to secure EHRs and facilitate telemedicine consultations. Patients can share their medical history securely with healthcare providers.
- Pharmaceutical Traceability: Companies like Pfizer and IBM are using blockchain to trace the provenance of pharmaceuticals, ensuring product authenticity and reducing counterfeit drugs’ circulation.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While blockchain offers immense promise in healthcare data management, it also faces challenges such as regulatory compliance, scalability, and integration with legacy systems. Additionally, addressing privacy concerns and ensuring patient consent mechanisms are user-friendly is crucial.
However, as blockchain technology continues to mature and gain acceptance, we can expect to see wider adoption in healthcare. It holds the potential to revolutionize how patient data is managed, shared, and secured, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and more efficient healthcare systems.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is ushering in a new era of healthcare data management. Its emphasis on security, privacy, interoperability, and patient empowerment has the potential to transform the healthcare industry. As blockchain applications continue to evolve and mature, we can anticipate a future where patients have greater control over their health data, healthcare providers collaborate more effectively, and the overall quality of care improves. The integration of blockchain technology is poised to revolutionize healthcare data management for the betterment of patients and healthcare professionals alike.